High-density interconnect (HDI) PCBs further develop upon this foundation, utilizing microvias, fine-line routing, blind and buried vias, and via-in-pad designs to achieve tighter component placement and high-speed performance within a compact size.
HDI PCB (High Density Interconnect PCB) is mainly used in compact, high-performance electronic products. Typical application fields include:
Consumer, Computer & Networking, Automotive, Medical.
| Feature | Capability | Feature | Capability |
| Via Types | Blind via, buried via, through-hole via | Min. mechanical drilling | 0.15mm |
| Number of layers | Up to 60 layers (evaluation required above 30 layers) | Min. laser drilling | Standard 4 mil, 3 mil require evaluation (corresponding to single 106PP). |
| HDI builds | 1+N+1, 2+N+2, ... , 6+N+6(≥6 orders require evaluation) | Max. laser drilling | 8 mil (corresponding dielectric thickness cannot exceed 0.15mm) |
| Copper weights( finished) | 18um-70um | Min. controlled depth drilling | PTH: 0.15mm; NPTH: 0.25mm |
| Min trace/spacing | 0.065mm/0.065mm | Aspect ratio | Max 14:1; evaluate if greater. |
| PCB thickness | 0.1-8.0mm (evaluation required for less than 0.2mm or greater than 6.5mm) | Min. solder mask bridge | 4mil(green, ≤1OZ) |
| Max. PCB dimension(finished) | 2-20 layers, 21*33 inches; length ≤ 1000mm; evaluate if short side > 21 inches | 5mil(other colors, ≤1OZ) | |
| Diameter range of resin-filled vias | 0.254-6.5mm |
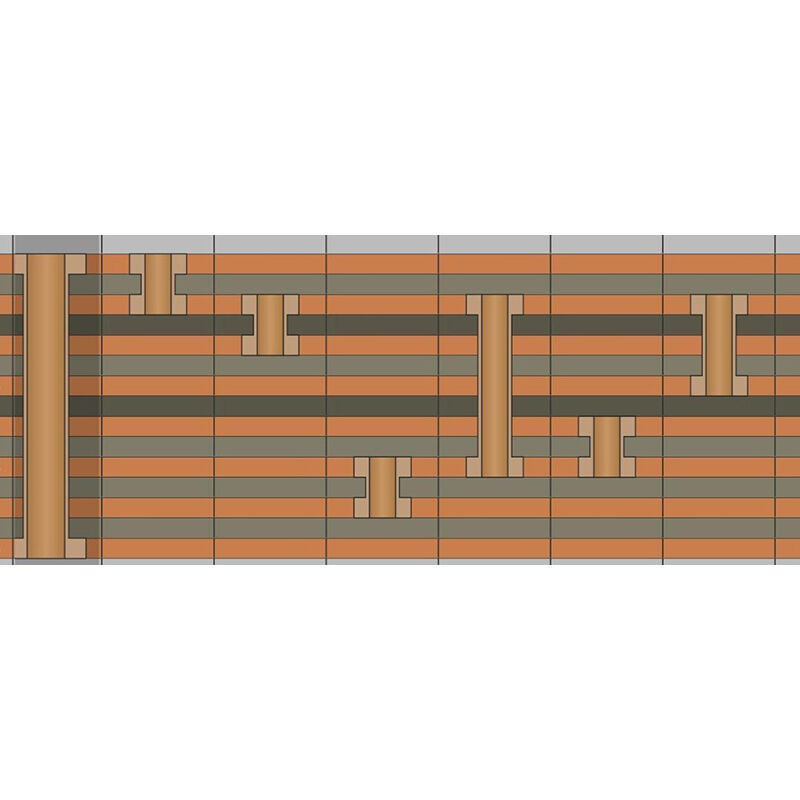
HDI PCB stack-up structures provide designers with greater flexibility in layer allocation, component placement, and routing options, enabling efficient utilization of available space and optimization of the PCB layout. The common HDI PCB stack-up structures are shown in the left diagram.